A list populated with double opt-ins is every email marketer’s dream. Customers coming this way are willing to commit and are more likely to stick around given a good experience. This article reveals how and when you can use double opt-in protocols to further your quest for email success.
The quality of your subscriber list is at the base of your hierarchy of needs as an email marketer. Without quality, you can’t climb to the upper layers.
As you’ll continue to add additional subscribers, you’ll find that your email list will need refinement as distilling your email list is crucial for the success of your operation.
You’ll need to employ strategies that convert your raw list of subscribers to segmented lists of committed, even engaged customers. These email recipients are the ones that will stick with you in the long run, recommend you to their friends, and return to your products again and again.
Using a double opt-in system powered by the sending of transactional emails to verify your subscribers’ emails and confirm their interest is an important first step toward building that quality subscriber list.
While double opt-in protocols add a little more friction and effort at the front end of your relationship with customers, the payoff is a list of subscribers who are willing to stick with you and that are less likely to churn and give your email reputation a burn.
After all, what good is a list of millions of subscribers if only a tiny percentage of them are genuinely interested in receiving your messages?
Closing the gap between interest and loyalty with double opt-in
When you’re asking for an email, you’re asking A LOT! It’s a bit ridiculous when you think about it.
You just met, the customer might be interested, but you’re asking them basically to rally to your flag without providing them more than a promise.
Loyalty, as you know, is hard to earn, but it can be done. People had been dealing with your problem from the days of yore.
During medieval times, kings and lords would seek out knights to serve them. Those who served as knights usually did so in exchange for payment–often in the form of land called a fief (a.k.a. fee)—a high-stakes win-win.
Recruiting and paying knights for their service was a competitive industry. Various landowners were regularly vying for territory and power. They needed to rally the support of these warriors for hire if they were to succeed.
Of course, if a king would trust a knight and grant him land or other treasure in exchange for his willingness to fight for his cause, that king would expect some proof of loyalty in exchange. Knights made a vow of allegiance to demonstrate their commitment. You know the rest.
Now, you don’t have a kingdom, yet you request access to your customers’ throne room—the inbox.
You are probably rethinking your odds at this point, right?
Don’t worry. Although no one will swear an oath of loyalty to your business, you can push them towards smaller commitments and gain their loyalty over time.
Small commitments drive economies.
Asking your customers to confirm their subscription through a double opt-in is such a commitment. This exchange:
- Adds a valid email address to your subscription list.
- Shows that the subscriber has an interest in your brand.
- And if you’re doing a good job, it provides value to your customers.
This article will walk you through the what, why, and how-to of using double opt-ins to refine your email marketing strategy.
Start at the top or leap ahead to find out how.
What’s a double opt-in?
Most of us are familiar with the single opt-in method for adding subscribers to our email lists. Single opt-ins occur when a customer takes some affirmative action that signals, “Yeah, sign me up, here’s my email.”
A single opt-in may be as simple as providing their email address or checking a box on your sign-up form or purchase page.
Once the consumer takes this first and only step, they are added to your mailing list.
Using a single opt-in strategy has become standard practice for most email marketers following the introduction of consumer protection and anti-spam laws around the globe.
Obtaining your customers’ permission to send them commercial emails through the single opt-in method is usually sufficient to demonstrate your compliance with the right to consent provisions of various regulations such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Single opt-in vs. double opt-in. What’s the difference?
Double opt-ins add an extra step to the sign-up process and an extra level of reassurance about the customer’s consent.
Instead of immediately adding new sign-ups to your list, you first send them a transactional email that asks them to confirm their subscription.
If you don’t receive a response to your request, then the recipient email isn’t added to your subscription list.
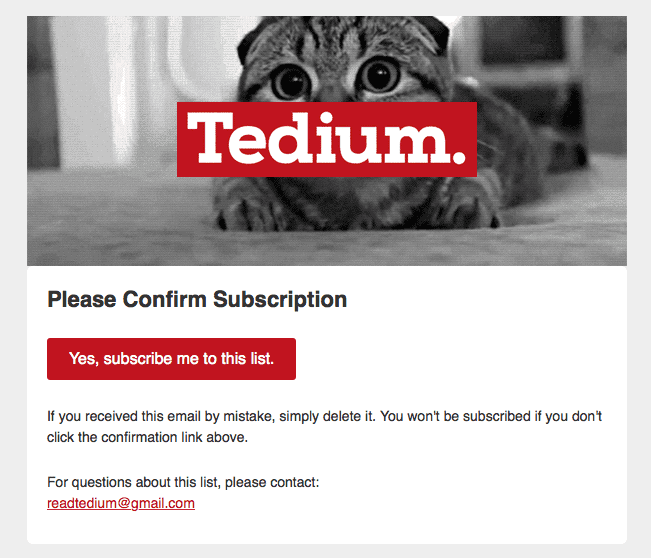
This simple, eye-catching opt-in email from Tedium explains the process to recipients, so there’s no doubt who’s in control.
Is double opt-in mandatory?
Current anti-spam laws don’t require double opt-ins. However, some email marketers in Germany favor using double opt-ins to demonstrate consumer consent as an extra precaution. For the rest of us, using double opt-ins remains completely optional.
What are the downsides of using double opt-ins?
There are downsides if you’re opting to hang out only with those who showed intent. Using double opt-in isn’t all mead and honey.
Double opt-ins add friction to your sign-up process, and friction can cause dropouts. Some of the people who signed up may forget or not bother to open your confirmation email, which will slow down your subscriber growth. If your double opt-in email lands in their spam folder, they may never even see it.
But then again, Nothing ventured; nothing gained!
Remember our kings and knights?
If they had traveled around, served some mead and meat, and shouted, “Who’s with me?” they probably would have gotten a lot of “Ayes!” But how many of those eager enlistees would have shown up on the battle day?
Single opt-ins give you an untested measure of interest in your brand. Double opt-ins give you proof of genuine commitment.
Of course, double opt-ins come at a cost beyond just the potential loss of forgetful or unengaged subscribers.
Much like those royal recruiters had to offer up land or treasure to win people to their cause, you’ll have to expend some resources upfront to implement a double opt-in program.
To affirm your subscribers’ commitment, you’ll need to:
- Send new sign-ups a transactional email with instructions for confirming their subscription.
- Create a landing page to direct recipients to complete the confirmation process.
- Set up a system to record your double opt-ins and remove non-responsive email addresses.
So why use double opt-ins?
Ultimately, when you implement a double opt-in system, you bet that quality over quantity will win the day.
Check out the following sections to discover how a double opt-in strategy improves your
- List accuracy.
- Deliverability.
- Engagement.
- Data.
Ready? Advance!
Why double opt-in is a good idea
At the beginning of this article, I mentioned the importance of subscriber lists. A good subscriber list is your gateway to sales, referrals, and revenue growth. A bad list? Well, they just consume time and effort without reward.
Worse, if the list is really bad, say it contains inaccurate or fake addresses, it can hurt your sender reputation and damper your deliverability.
It keeps your list clean
Inaccurate or invalid emails can come to you by accident or on purpose. Either way, you don’t want these emails on your subscriber list as they can lead to hard bounces and get you placed on ISPs’ naughty list.
Address verification helps you avoid unintentional errors, such as a customer who entered their email incorrectly. It can also help you detect bot-driven spam trap addresses intended to catch bulk emailers who don’t practice proper list hygiene.
There are a few ways to verify email addresses either before or after they are added to your subscription list in addition to double opt-ins.
These methods include:
- Hidden form fields. These are fields that you include in your sign-up forms’ code but aren’t visible to humans who view the sign-up form.
Only bots that are up to trouble (like attempting to submit fake or spam trap emails) will detect and fill in these bot boxes. Automate the process of spotting and eliminating any emails with an associated hidden field completed to dodge these traps.
- Sign-up form CAPTCHAs. Does anybody not hate CAPTCHAs? Is that a light post? Is that a letter or a number? Arghh! Refresh and try again.
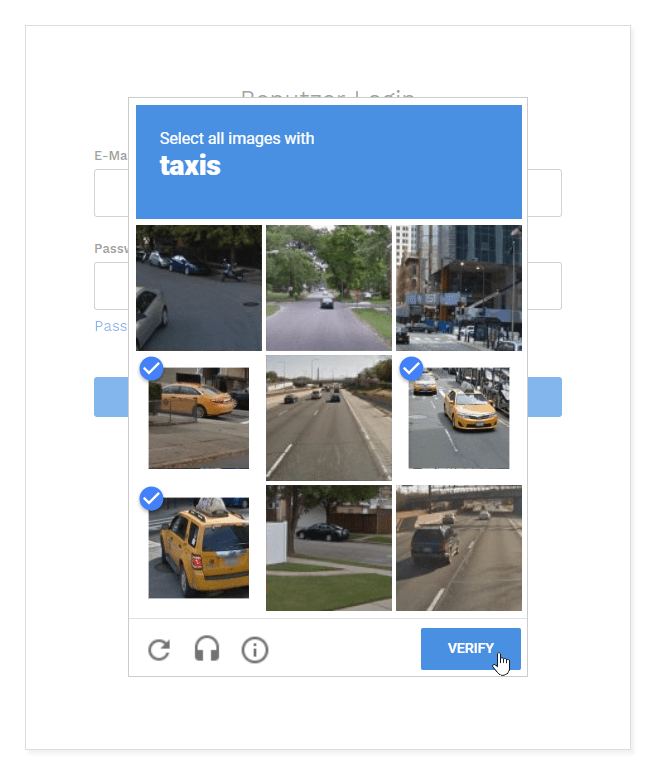
CAPTCHAs can help you avoid bots, but talk about friction. You may lose real customers who don’t have time to `play games.’
- Real-time email validation. Now we’re getting somewhere. Real-time email validation allows you to check an email at the moment of sign-up. If your customer enters an invalid email, the sign-up process is interrupted, and they are asked to correct it.
While this does add a little friction–mainly if the error message is unclear–it’s fast and effective. Real-time email validation isn’t free. You’ll pay a per-subscriber fee to access this verification service.
- Bulk email verifications. While not as immediately gratifying as real-time email validation, bulk verifications are still a solid strategy to help you keep your email lists clean. You’ll still have to pay a fee to have a vendor check each email, but you can decide how often you want to perform these checks.
These alternatives are great, but double opt-ins are still our favorite list defender.
Sending a confirmation email as part of your double opt-in program moves your customer forward in their relationship with your brand. You get verification plus interaction.
If you want to double-up on your email verification processes, use one of these measures along with your double opt-in program as part of a multi-method email hygiene program.
Deliverability is improved
The engagement your double opt-in emails generate is good for your deliverability. Each positive response represents an open and a click, communicating to ISPs that their users welcome your emails.
However, sending email messages to invalid or non-subscriber addresses is bad for your sender reputation. Even worse is having your messages marked as spam. Racking up spam complaints is a one-way ticket to destroy your sender reputation.
Don’t let spam complaints sink your reputation
Why would someone mark your emails as spam after they signed up to receive them?
First, people forget. If you aren’t sending a timely confirmation, your new subscriber may forget that they signed up by the time your first message arrives.
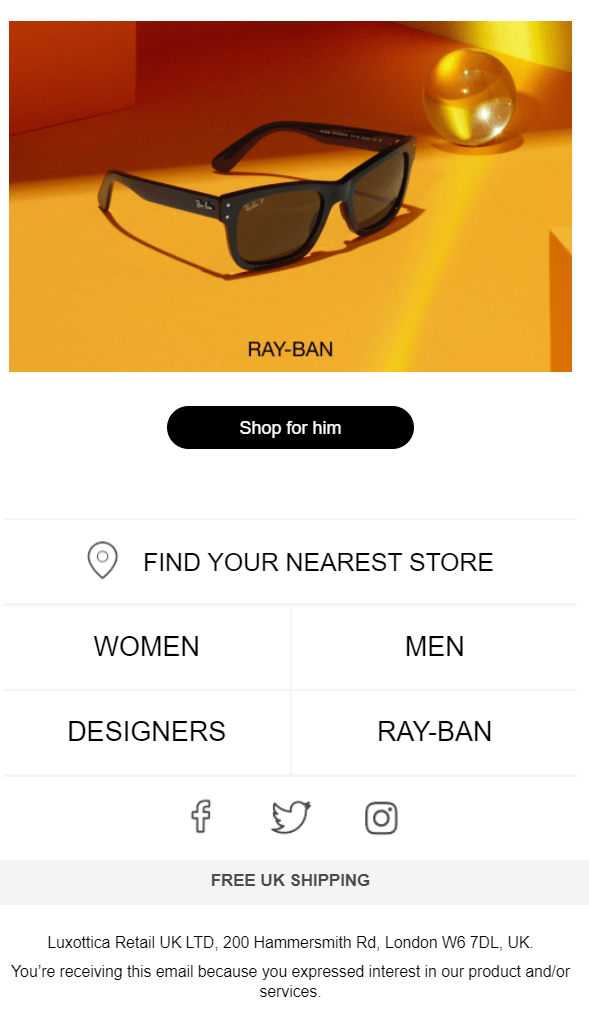
This is one reason we recommend that you include a “Why am I receiving this email message” in your emails’ footers, as the Sunglass Hut has in this update.
Second, occasionally, someone may submit an email that isn’t their own. Maybe they entered a fake email address, and it turns out it belongs to someone else. Or, perhaps, they are intentionally using someone else’s address. How unchivalrous!
Prevent potential spam complaints by waiting until you’ve received your double opt-in confirmation before sending marketing content to new addresses.
This friendly message from Spotify lets the recipient decide when and if they want to continue this budding relationship.

Prevent unnecessary unsubscribers
Refreshing your recipients’ memories with a double opt-in message and asking them to affirm their interest will also reduce your unsubscribe rates.
Unsubscribes are a natural part of the email marketing lifecycle. People’s tastes and needs change, and they may fall out of love with your content at some point. But they’ll stick around a lot longer if they were genuinely interested in your content in the first place.
Make sure your churn rate isn’t inflated by the presence of recipients who were never really that into you.
You get to nurture engagement from the start
Used effectively, your confirmation message adds a positive touchpoint along your customer’s journey. It’s an opportunity to present your brand, build trust and continue the conversation with a new subscriber.
Zulily’s cheerful email sets just the right tone for a winning relationship.

Getting off to a good start is good for your business.
We’ll dig deeper into this topic in the next section.
Double opt-ins are also a quick way to evaluate the value of a new email lead.
Conversely, a customer who doesn’t respond may signal that they aren’t a high-value lead. They may have provided an email address solely to complete a purchase or download your lead magnet and don’t want to engage further.
Double opt-ins improve the quality of your performance data
Using double opt-in provides you with precise performance data that allows you to make improvements faster. Instead of wading through vanity metrics, you can get straight to the good stuff.
Consider this.
If you send emails to a list of 500,000 subscribers and get a click rate of 5%, you’ll probably want to figure out what you could do better. Where do you start your evaluation?
If your email list was generated from single opt-in sign-ups, you’d need to start by examining the validity of your emails. Then, you’ll need to look at the customer data to determine if there are any signs of interest connected to that email. How many of those 500,000 subscribers were good candidates for your campaign?
Only after you’ve answered these questions can you move on to evaluating deliverability, content, and other issues.
On the other hand, if you know that your list includes only verified emails of subscribers who have double opted-in, you can jump ahead in your evaluation. Is there something in the messages causing them to be screened by ISPs? Was your subject line a fail? Did you optimize your send time?
This reasoning applies to other performance data as well. Evaluating what went wrong with unqualified or low-value leads won’t answer questions about how to convert genuine customers.
Is a double opt-in the right strategy for you?
As you’ve probably figured out by now, we’re fans of the double opt-in. In exchange for a little extra effort, you get better qualified, more engaged leads and an opportunity to make a great first impression.
We’re big fans of data, too. So, if you aren’t sure if the benefits outweigh the costs, do some testing. Set up a double opt-in program for some of your new sign-ups and track your responses and engagement for those subscribers compared to your single opt-in customers. Use our guide to the email metrics that matter to help you decide what data to track.
Follow the best practices detailed below to ensure that your double opt-in program is optimized for success.
Implement an irresistible double opt-in plan with these best practices

When kings and lords set out to recruit knights to support them in battle, they faced some hurdles. First, other nobles were vying for the loyalty of those same knights. Plus, not everyone was eager to pledge their time and skills. Getting that critical commitment meant making an attractive offer. The king who best mastered the art of persuasion often prevailed.
Similarly, you’ll need to employ persuasion skills and make your opt-in offer attractive to maximize the number of subscribers you win.
The following strategies will serve you well in the days ahead.
Tell people what to expect
The entire idea of double opt-in is about commitment. And commitment stems from trust and transparency–from both sides.
This means that you need to be there for the subscribers in every step of the process, letting them know what happens next and what they have to do to advance the process. Do they need to check the inbox now? Click a link later?
Keep your explanation simple and uncomplicated
Explain your process on your sign-up form, in an overlay or pop-up, or on the post-sign-up thank you page. Let people know that you’ll be sending them a follow-up email and why.
Here’s how Ongage does:
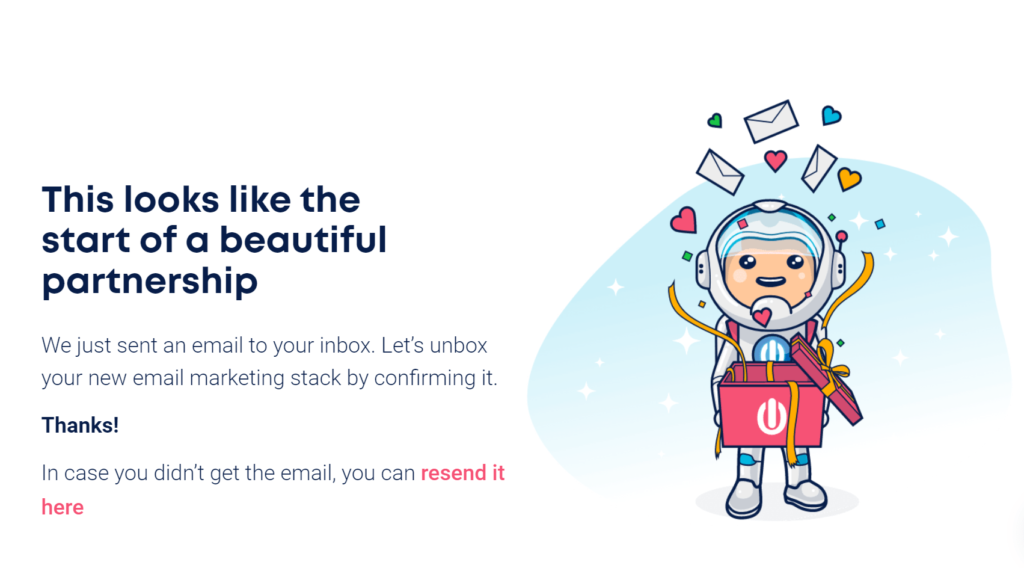
Then, refresh your subscriber’s memory by explaining again in the confirmation email that you send.
Chipotle’s email reiterates their double opt-in instructions and reminds recipients of the brand’s iconic food offering.

Strike while the iron is hot
An excellent medieval blacksmith knew that if you failed to act in the critical moment after removing your metal from the fire, your efforts to craft a sword would fail.
Your effort to gain a commitment may fail if you miss your critical window to act as well.
The best time to send a confirmation email is immediately after someone has signed up to be a subscriber.
Sending your confirmation right away is your best chance of catching your subscriber when they
- Are online and active.
- Are expecting (or maybe even be checking for) your email.
- Haven’t forgotten why they signed up for your email list.
Our email automation tools make it easy for you to make sure your double opt-in request is delivered at lightning speed. We explain how to make it happen in the next section.
Clearly state your purpose in your subject line
Consumers receive many emails each day and delete many of them without ever viewing the contents. Your subscribers must receive and open your confirmation message for your double opt-in program to work.
On average, transactional emails have a higher open rate than marketing emails. But you still need to do your part to ensure those opens by making the purpose of your email clear in your subject line and preview text.
Use language such as:
- “Confirm your subscription.”
- “Activate your account.”
- “Action requested.”
- “One more step to…”
along with a message in your brand style to convey the purpose of your email.
Be sure that your sender name is recognizable, too. Consider using the BIMI protocol to display your logo along with your sender name. Remember, securing a commitment requires transparency and trust.
Strategy 4: Keep your (and your subscriber’s) eye on the prize
At the start of a new relationship, it can be tempting to present all your best assets. But when it comes to transactional emails, sometimes less is more.
Incorporating your brand voice and graphics into your opt-in email is okay, but don’t overdo it. Your relationship will end before it begins if your recipient doesn’t click your confirmation link.
Make sure that CTA is front and center to cut out any clutter.
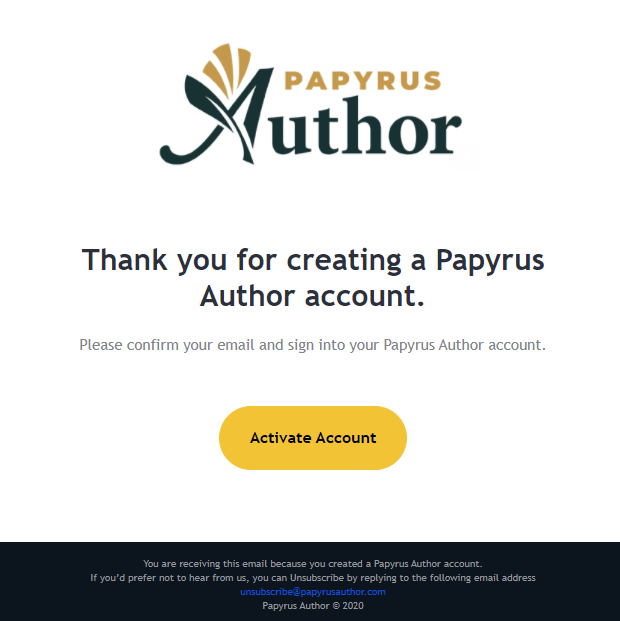
Papyrus uses simple language and bold color to direct their customers’ attention to the desired action.
Incentivize taking the next step
When you ask someone to do something for you, it helps offer something in return. For example, to get knights to commit to their cause, kings had to pay a fee–usually in the form of land.
You don’t have to give away the farm to get people to confirm their email subscriptions, but a little incentive that provides some sort of value never hurts.
Remind subscribers of the benefits they’ll gain when they activate their email, such as the opportunity to participate in loyalty programs or download additional content.
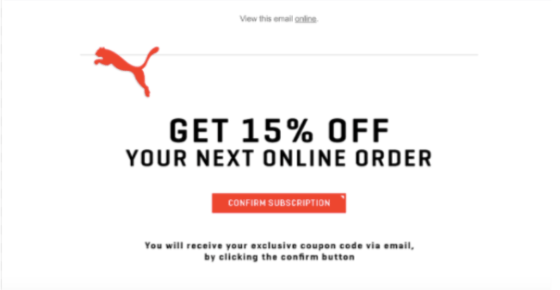
Or make them a direct offer in exchange for their click like Puma has done in this email.
Give your customers choices
Did you know that it wasn’t just knights who were asked to serve their medieval rulers? Tenants who grew crops, tended livestock, or offered a skilled trade might also commit to a particular noble. Not everyone is a warrior. Even in the feudal system, it was good to have options.
It’s good for your subscribers to have options, too. Tell your new email recipients about yours.
Maybe your email recipients want to receive fewer emails or just certain types of messaging. Making sure your subscribers have choices can make the difference between saying yes to a commitment or signing off forever.
Use or more of the following methods to communicate your customer-friendly options to your new email recipients:
- Create a preference center on your website. Then, include a link to that page in the footer of your emails.
- Include a message on your unsubscribe confirmation page informing customers that they can choose to adjust their preferences instead.
- Mention your preference center and share a link in the body of your confirmation email.
- Send a follow-up email that includes an interactive preference center.
Matches Fashion gives its subscribers plenty of options to choose from, maintaining engagement while putting them in control of their inbox.

Your preference center is also a valuable source of data for you. Which options do most of your new subscribers select? Which ones does everyone avoid?
Use the information you gain from your customers’ input to develop more effective, customer-friendly campaigns.
Keep the momentum going with a welcome email
While both are event-triggered, a double opt-in email is not the same as a welcome email. The double opt-in permits you to continue the conversation. Your welcome email is how you do that.
Like transactional emails, welcome emails tend to have good engagement. Send yours soon after you receive your subscriber’s opt-in response to get your relationship off to a good start. When you send your welcome message, be sure to include links to any promised resources. Maybe add a surprise or two, such as a welcome discount or value-adding content.
Your welcome email is also the perfect place to introduce your preference center and share other onboarding tips with new subscribers.
Airtable incorporates a short video and shares how-to guides with its fresh subscribers to ensure that their new relationship goes smoothly.
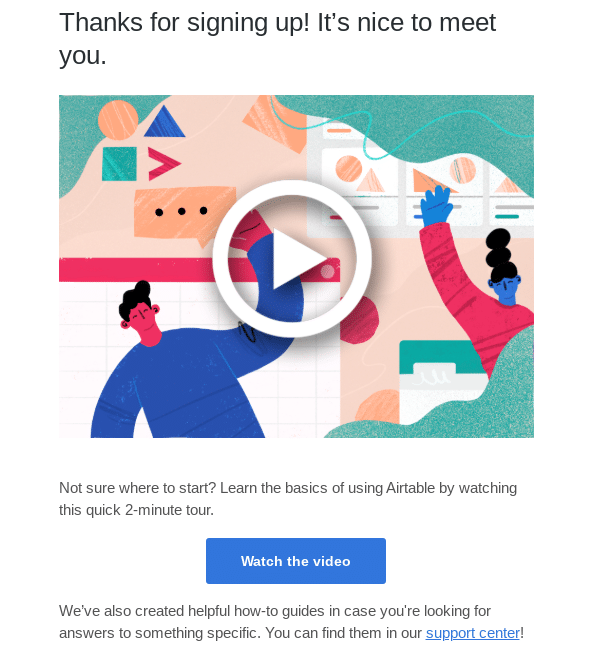
Incorporate your double opt-in program into the big picture
As email marketers, we often think about how each email in a sequence can impact the customers’ behavior. For an engagement super-boost, go omnichannel. Extend your thinking and customer experience strategy to every touchpoint across your marketing channels.
Coordinate the messaging across your Thank You page, preference center, welcome, and other follow-up emails so that you serve your new subscribers well and always add value.
#4 How to implement double opt-in in Ongage
As speed is of the essence when it comes to opt-in emails, we recommend sending these transactional messages using the flexible Ongage email API combined with our Automation Rules module.
Here’s how:
- Create a new list field to designate the opt-in status of the user. Use “blank” as a default value. This will then become one of the up to 150 data points that you can assign to each user using Ongage.
- Create your double opt-in email via Ongage’s built-in functionality. Once activated, this email will be sent to every new subscriber you import into Ongage.
- Your email’s CTA will include a link that looks something like this:
<a href=" https://www.mywebsite.com?ocxf_confirm=Yes "> Click here to confirm </a>In this example, the opt-in field is labeled “confirm.” A click on the CTA registers a “yes” in that field.
- Once a user’s opt-in status becomes a yes, they can receive any other emails you’ve included in your sequence. We recommend using the Ongage Automation Rules module to trigger the immediate sending of a welcome email.
You’ll also need to set up an API call from your webform or CRM to ensure that each subscriber is imported into Ongage immediately and quickly receives the double opt-in email.
When a user signs up via one of your channels, make an automatic POST request from your CRM or web form to: https://api.ongage.net/api/v2/contacts/.
Use a JSON payload, like the following example:
{ "email": "john@doe.com", "name": "John Doe", "country": "Chile" }Of course, if you need help setting up your double opt-in automation, get in touch! We’re here to help.
Gather a mighty army of subscribers with double opt-in for email
Committed customers are high-value customers. Focus on your best leads with the double opt-in tips we’ve shared in this article.
With double opt-in, you can start as you mean to go on with a list full of customers who
- a) exist,
- b) are engaged with their inbox, and
- c) are prepared to take that extra step to get on your email list.
Then, to win the battle for customers’ loyalty and dollars, leverage data, and technology to craft engaging emails that hold their interest.
Need some fresh advice on how to maintain your customers’ attention? Check out our guide, Improving Email Deliverability Through Engagement.